Mounjaro vs. Wegovy: The Verdict on the Best Weight Loss Medication
Table of Contents
What is Mounjaro?
Mounjaro, scientifically known as Tirzepatide. It has shown significant promise in aiding weight loss. Manufactured by Eli Lilly and Company, Mounjaro operates through a unique mode of action that sets it apart from existing weight management treatments.
Unlike traditional medications, Mounjaro targets both the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor and the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor. This dual action approach enhances the body’s natural ability to regulate blood sugar levels and promotes weight loss. Clinical studies have demonstrated that Tirzepatide effectively reduces blood sugar levels and, importantly, aids in substantial weight reduction in patients when combined with a healthy diet and exercise.
What is Wegovy?
Wegovy is a prescription medication designed to aid in weight loss, primarily for adults struggling with obesity or weight-related medical conditions. Clinically known as semaglutide, Wegovy mimics a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) that targets areas in the brain responsible for regulating appetite and food intake. This mechanism of action helps reduce hunger and increase feelings of fullness, leading to a decrease in calorie intake and, consequently, weight loss
Approved by health authorities for its effectiveness and safety, Wegovy has shown promising results in clinical trials, significantly aiding individuals in their weight loss journey. By adjusting the body’s natural hunger signals, Wegovy empowers patients to achieve and maintain a healthier weight, which can greatly reduce the risk of weight-related health issues, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
Comparing the effectiveness of Mounjaro vs Wegovy: clinical trials and studies
The clinical studies for Wegovy (Semaglutide) and Mounjaro (Tirzepatide) offer comprehensive data on their efficacy in treating obesity, highlighting significant advances in pharmacological interventions for weight management. Each drug demonstrates a unique profile of effectiveness, with varying degrees of weight loss and improvements in cardiometabolic risk factors among participants with obesity or overweight. Here, we delve into the details of their efficacy as presented in the clinical trials.
Wegovy (Semaglutide)
Wegovy, a once-weekly injectable treatment, was evaluated in a 68-week clinical trial involving adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater, or 27 or greater with at least one weight-related coexisting condition, but without diabetes. The core findings from the study regarding its efficacy include:
- Weight loss: Participants receiving Wegovy experienced a mean weight reduction of 14.9% from their baseline body weight. This outcome significantly surpassed the placebo group’s mean weight loss of 2.4%, translating into an estimated treatment difference of 12.4 percentage points. The substantial weight loss observed with Wegovy underscores its potential as a powerful tool in weight management strategies.
- Achievement of weight loss goals: A remarkable 86.4% of Wegovy-treated participants achieved a weight reduction of 5% or more, a widely recognized threshold for clinically meaningful weight loss. Furthermore, 69.1% and 50.5% of participants reached weight loss milestones of 10% and 15%, respectively, highlighting the drug’s ability to support significant weight reduction goals.
- Cardiometabolic improvements: Alongside weight loss, Wegovy-treated participants saw notable improvements in various cardiometabolic risk factors. These included reductions in waist circumference, systolic blood pressure, and favorable changes in lipid profiles, all of which contribute to a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases and other obesity-related conditions.
Mounjaro (Tirzepatide)
Mounjaro was assessed in a 72-week clinical trial involving adults with obesity or overweight, excluding those with diabetes. The trial’s outcomes on Mounjaro’s efficacy are as follows:
- Weight loss: The mean percentage changes in weight at week 72 were −15.0%, −19.5%, and −20.9% for the 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg doses of Mounjaro, respectively, compared to −3.1% for the placebo. These results indicate a dose-dependent efficacy in weight reduction, with the highest dose achieving nearly 21% mean weight loss from baseline.
- Achievement of weight loss goals: Across the dosage groups, a significant portion of participants achieved substantial weight loss, with 85% to 91% of individuals reaching a reduction of 5% or more in body weight. The rates of participants achieving higher thresholds of weight loss, such as 20% or more, were also notably high, especially in the 15 mg dose group.
- Cardiometabolic improvements: Similar to Wegovy, Mounjaro showed significant improvements in cardiometabolic risk factors. Participants experienced reductions in waist circumference and improvements in lipid profiles and blood pressure levels. These changes are beneficial for reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improving overall metabolic health.
Comparative Efficacy
When comparing the efficacy of Wegovy and Mounjaro, several key points emerge:
- Degree of weight loss: Both medications demonstrate a high efficacy in promoting weight loss, with Mounjaro showing slightly superior results, especially at higher doses. The differences in mean weight reduction percentages suggest that Mounjaro may offer an edge for individuals seeking more substantial weight loss.
- Consistency across dose ranges: Mounjaro’s efficacy appears to increase with the dosage, providing flexibility in managing treatment based on individual responses and tolerability.
- Cardiometabolic risk reduction: Both drugs not only support significant weight loss but also contribute to substantial improvements in cardiometabolic health, indicating their potential to address the broader spectrum of obesity-related health risks.
In conclusion, both Wegovy and Mounjaro represent significant progress in the pharmacological treatment of obesity, with robust clinical trials demonstrating their efficacy in promoting significant weight loss and enhancing cardiometabolic health. Mounjaro, with its dose-dependent effectiveness, shows a slightly superior efficacy in weight reduction, offering a promising option for individuals with obesity or overweight seeking substantial weight loss. The choice between Wegovy and Mounjaro should consider individual patient needs, tolerability, and specific health goals, making personalised treatment strategies paramount in the management of obesity.
Mounjaro and Wegovy dosing schedules and administration
Mounjaro (Tirzepatide)
Indication: Mounjaro is is approved for weight management in adults with obesity (initial Body Mass Index [BMI] of 30 kg/m² or more) or overweight (initial BMI of 27 kg/m² or more) in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbidity, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or dyslipidemia, as part of a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
Dosing schedule:
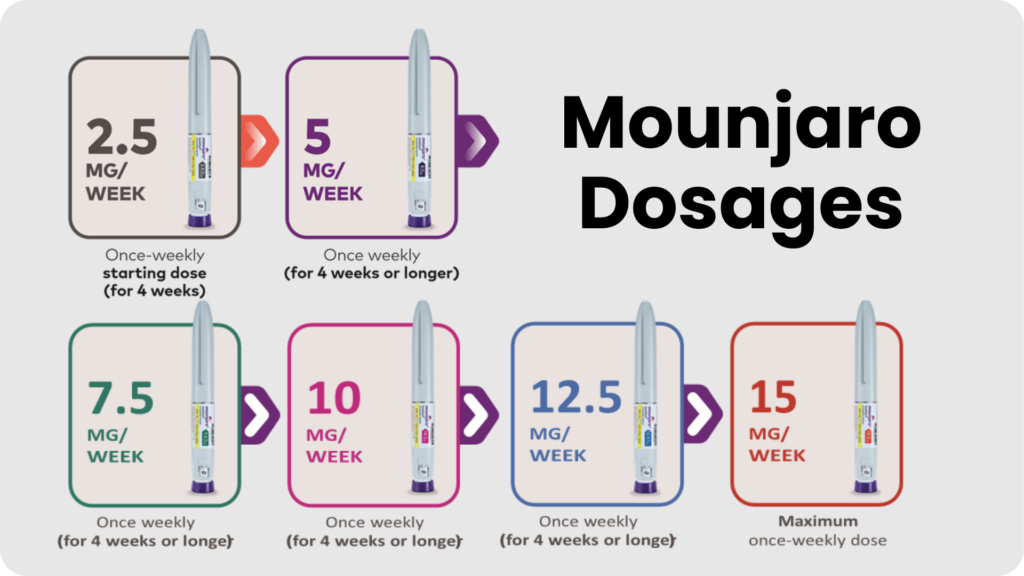
- Initiation: The recommended starting dose is 2.5 mg once weekly.
- Titration: The dose should be increased to 5 mg once weekly after 4 weeks.
- Maintenance: The dose can be further adjusted based on therapeutic response and tolerability, typically at intervals of 4 weeks, to a maximum of 15 mg once weekly.
Administration:
- Mounjaro is administered via subcutaneous injection. It can be injected into the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
- The injection can be done at any time of the day, with or without meals.

Wegovy (Semaglutide)
Indication: Wegovy is also approved for weight management in adults with obesity (initial Body Mass Index [BMI] of 30 kg/m² or more) or overweight (initial BMI of 27 kg/m² or more) in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbidity, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or dyslipidemia, as part of a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
Dosing schedule:
- Initiation: The starting dose is 0.25 mg once weekly for 4 weeks.
- Titration: The dose is gradually increased over several months to the target dose of 2.4 mg once weekly. The titration steps are 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 1.7 mg, and then 2.4 mg, each for 4 weeks.
Administration:
- Wegovy is administered through a subcutaneous injection. Similar to Mounjaro, it can be injected into the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
- The injection timing is flexible and can be done at any time of the day, with or without meals.
Comparative analysis
- Dosing flexibility: Both medications use a titration approach to reach the effective dose, minimising side effects and improving tolerability.
- Administration route: Both are administered via subcutaneous injection, offering similar convenience and patient self-administration capability.
- Indications: Mounjaro and Wegovy are focused on obesity and weight management, with benefits seen in patients with weight-related comorbidities, including improvements in glycaemic control for those with type 2 diabetes.
- Mechanism of action: While both medications work by mimicking the effects of GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1), contributing to reduced appetite and improved insulin secretion, Mounjaro (tirzepatide) also mimics the effects of GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide), offering a dual approach to managing weight.
In conclusion, while Mounjaro and Wegovy share similarities in their administration and use in treating conditions related to metabolic syndrome, their indications, dosing regimens, and specific patient populations, they cater to differ.
Mounjaro vs. Wegovy: Price Analysis
When considering weight management solutions, patients often compare options such as Mounjaro and Wegovy, both available through The Family Chemist. Understanding the cost implications of these treatments is crucial for making an informed decision. Here’s a comparative analysis of Mounjaro and Wegovy based on their pricing at The Family Chemist, designed to aid your decision-making process.
Mounjaro and Wegovy are injectable medications prescribed for weight management, with their pricing varying based on dosage. Below, we break down the costs associated with each, providing a clear comparison for patients.
Mounjaro injection pen pricing
| Dosage (mg) | Price (£) |
| 2.5 | 149 |
| 5 | 155 |
| 7.5 | 169 |
| 10 | 169 |
| 12.5 | 185 |
| 15 | 185 |
Wegovy injection pen pricing
Dosage (mg) | Price (£) |
| 0.25 | 145 |
| 0.5 | 149 |
| 1 | 159 |
| 1.7 | 215 |
| 2.4 | 245 |
Cost implications for patients
When comparing Mounjaro and Wegovy, it’s evident that initial costs for starting doses are quite similar, offering flexibility for patients beginning their weight management journey. However, as the treatment progresses, the cost of Wegovy increases, particularly for higher doses required in later weeks.
For Mounjaro, the price increases are more gradual across different dosages, making it a potentially more cost-effective option for long-term use, especially for patients prescribed higher doses.
Comparing how Wegovy and Mounjaro work
How Mounjaro works
Mounjaro (Tirzepatide) is a prescription medication that targets both the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptors. This dual-action approach helps promotes weight loss. By activating these receptors, Mounjaro reduces hunger, leading to a decrease in calorie intake.
Wegovy’s mode of action
Wegovy (Semaglutide), on the other hand, focuses solely on the GLP-1 receptor. Similar to Mounjaro, it curbs appetite. However, Wegovy’s singular focus on the GLP-1 receptor means it specifically targets the pathways related to hunger and satiety, making it a potent option for significant weight loss.
Comparing side effects of Mounjaro and Wegovy
The side effect profiles of Mounjaro (Tirzepatide) and Wegovy (Semaglutide) as reported in their respective clinical trials . Both medications share common side effects, typical of GLP-1 receptor agonists, with gastrointestinal events being the most prominent. However, the intensity, frequency, and specific types of side effects can vary between the two, impacting patient tolerance and treatment adherence. Below is a detailed comparison of their side effect profiles based on the trials discussed.
Gastrointestinal side effects
- Mounjaro: Gastrointestinal adverse events were the most common side effects reported, including nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting, and constipation. These were generally mild to moderate in severity and primarily occurred during the dose-escalation period. The trials noted a dose-dependent increase in the occurrence of gastrointestinal side effects, suggesting that higher doses of Mounjaro are associated with an increased likelihood of these adverse events. Treatment discontinuation due to adverse events was observed, with rates varying across the different dosage groups.
- Wegovy: Similar to Mounjaro, gastrointestinal side effects were also the most frequently reported adverse events in Wegovy trials, with nausea, diarrhoea, constipation, and vomiting being prevalent. These events were typically transient and mild-to-moderate in severity, subsiding over time. The occurrence of gastrointestinal side effects contributed to a higher rate of treatment discontinuation among Wegovy recipients compared to the placebo group, although the specific rate was not provided in the summary.
Serious adverse events
- Mounjaro: The trial summary for Mounjaro did not specifically mention the rate of serious adverse events but noted that adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in a small percentage of participants across all tirzepatide doses.
- Wegovy: Serious adverse events were reported in both the Wegovy and placebo groups, with a slightly higher incidence in the Wegovy group. Specific serious gastrointestinal disorders and hepatobiliary disorders were noted, contributing to the overall serious adverse event rate.
Specific side effects
- Mounjaro: Besides gastrointestinal side effects, the trial summary did not detail other specific side effects or the comparative incidence of serious adverse events versus the placebo.
- Wegovy: Aside from gastrointestinal issues, Wegovy trials highlighted gallbladder-related disorders (primarily cholelithiasis) as more common in the Wegovy group than in the placebo group. Additionally, mild acute pancreatitis was reported in a few participants, which was a concern given the link between GLP-1 receptor agonists and pancreatitis.
Treatment discontinuation due to adverse events
- Mounjaro: Discontinuation rates due to adverse events varied by dose, indicating a dose-dependent relationship between tirzepatide and the likelihood of discontinuing treatment due to side effects.
- Wegovy: A certain percentage of participants discontinued Wegovy due to adverse events, which were mainly gastrointestinal in nature. The specific discontinuation rate was higher in the Wegovy group compared to placebo, underscoring the impact of side effects on treatment adherence.
Summary of side effect comparison
Both Mounjaro and Wegovy demonstrate a side effect profile characterised predominantly by gastrointestinal adverse events, consistent with the GLP-1 receptor agonist class of medications. The occurrence of these side effects is generally mild to moderate and transient but can lead to treatment discontinuation in a subset of patients. Mounjaro’s side effects appear to be dose-dependent, with higher doses associated with an increased frequency of gastrointestinal issues. Wegovy, while also exhibiting a similar profile of side effects, has additional concerns regarding gallbladder-related disorders and a small number of pancreatitis cases.
The decision to use Mounjaro or Wegovy for obesity management should consider these side effect profiles, balancing the benefits of weight loss and cardiometabolic improvement against the potential for adverse events and their impact on patient well-being and treatment adherence.
The Verdict
When comparing Mounjaro and Wegovy, it’s clear that both medications offer substantial benefits for weight management. Mounjaro’s dual-action mechanism potentially provides an edge in achieving more significant weight loss. However, Mounjaro’s side effects appear to be dose-dependent, with higher doses associated with an increased frequency of gastrointestinal issues. The choice between these two should be tailored to individual patient needs, considering factors such as specific health goals and medication tolerance.
FAQs
Can I switch between Wegovy and Mounjaro?
FAQs
Can I switch between Wegovy and Mounjaro?
Considering a change from Wegovy® to Mounjaro® requires careful thought, despite studies suggesting Mounjaro® may offer enhanced effectiveness. For individuals who have been using Wegovy® over a period and are managing its side effects well, particularly those experiencing positive outcomes, continuing with Wegovy® could be the most beneficial approach. For those contemplating a switch, guidance from healthcare professionals, such as those at The Family Chemist, is crucial. We can provide personalised advice based on your health records if you’re already a patient or assist in making a clinically appropriate transition if you’re considering becoming one. Regardless of your current treatment path, a thorough weight loss consultation is essential to ensure the best course of action for your health goals.
Can I use both Wegovy and Mounjaro together?
No, it is not advisable to use Wegovy and Mounjaro simultaneously. These medications, each approved for the management of obesity or type 2 diabetes, are designed to be used individually. Using both medications together could lead to an increased risk of adverse effects and is strongly discouraged.
Is Mounjaro and Wegovy the same?
While Mounjaro and Wegovy are used to treat similar conditions, they are not the same medication. Mounjaro (tirzepatide) is a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, which is a newer class of medication. Wegovy (semaglutide) is a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Their differences lie in their mechanisms of action and potentially in their efficacy and side effect profiles.