What Are Mounjaro Side Effects And How To Overcome Them
Table of Contents
What is Mounjaro?
Mounjaro is a breakthrough prescription drug known for its weight management benefits, marking a significant leap in obesity treatment. Its key component, Tirzepatide, introduces a unique approach by emulating the functions of two essential hormones, thus standing out from existing weight loss drugs. It effectively controls food intake and sugar levels by enhancing GLP-1 hormone actions, which delay stomach emptying to extend fullness and reduce hunger. This process lowers calorie consumption. Furthermore, Tirzepatide boosts insulin release and curbs glucagon production, alongside influencing GIP hormone activity to regulate insulin secretion and fat metabolism, offering a comprehensive approach to weight loss.
What are the common side effects of Mounjaro?
Mounjaro has been gaining attention for its effectiveness. However, like all medications, it comes with its own set of potential side effects. It’s crucial for patients and The Family Chemsit’s pharmacist to be aware of these possible reactions to better manage and mitigate them.
Low blood sugar
One of the common side effects, affecting up to 1 in 10 people, is low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), especially when Mounjaro (tirzepatide) is used alongside metformin and a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, another type of diabetes medication. Symptoms of low blood sugar can include headache, drowsiness, weakness, dizziness, hunger, confusion, irritability, a fast heartbeat, and sweating. Decreased appetite is also observed in patients treated for type 2 diabetes, which could contribute to the drug’s effectiveness in weight management but also requires monitoring to ensure nutritional needs are met.
How to overcome low blood sugar:
Managing low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) involves both immediate steps to raise blood sugar levels back to normal and strategies to prevent it from occurring in the first place. Here are some tips and strategies you might find helpful for your patients:
Immediate steps for low blood sugar
- Consume fast-acting carbohydrates: When blood sugar levels drop, consuming 15-20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates is crucial. Examples include glucose tablets, fruit juice, regular (not diet) soda, honey, or candy. Recheck blood sugar levels after 15 minutes and repeat if necessary until blood sugar levels are back to normal.
- Avoid foods with fat: Eating foods high in fat to treat low blood sugar can delay the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream. It’s better to stick with simple carbs.
- Once stable, eat a small snack: If it’s going to be a while before the next meal, eating a snack that includes protein and complex carbohydrates (like half a sandwich) can help stabilise blood sugar levels.
Preventing low blood sugar
- Regular meal times: Encourage eating small, frequent meals throughout the day to stabilise blood sugar levels.
- Monitor blood sugar levels: Regular monitoring can help your patients recognise the signs of low blood sugar and take steps to prevent it.
- Adjust medications if necessary: Work with healthcare providers to adjust insulin or other diabetes medication doses to prevent low blood sugar episodes.
- Exercise smartly: Advise eating a small snack before exercising to prevent hypoglycaemia, especially if insulin levels have been adjusted for exercise.
- Educate on symptoms: Ensure your patients know the symptoms of low blood sugar, including shaking, sweating, hunger, dizziness, and mood changes, so they can act quickly.
- Alcohol consumption: If consuming alcohol, advise to do so with food to avoid a drop in blood sugar levels later.
- Emergency glucose: Advise carrying glucose tablets, gels, or other forms of quick sugar at all times, especially if they are prone to episodes of hypoglycaemia.
- Medical ID: Recommend wearing a medical ID bracelet or carrying a card that lets others know they have diabetes in case of an emergency.
Long-term management
- Dietary planning: Work with a dietitian to create a meal plan that helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Manage stress: Stress can affect blood sugar levels, so practicing stress-reduction techniques can be beneficial.
- Regular check-ups: Regular visits with healthcare providers are essential to monitor and manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions, presenting as rash, itching, or eczema, are also a possible side effect. Stop using Mounjaro if you experience an allergic reaction and seek advice from The Family Chemist clinician or GP.
Acid reflux
Other digestive issues such as stomach pain, indigestion, bloating, burping, gas, and reflux or heartburn (GORD) have been reported. These side effects could affect a patient’s quality of life and might require adjustments in treatment or additional medications to manage these symptoms.
 How do you overcome reflux?
How do you overcome reflux?
Overcoming stomach pain, indigestion, bloating, burping, gas, and reflux or heartburn, collectively known as Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD), requires a multifaceted approach that involves dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and possibly medical treatment. Here are several tips to help manage these symptoms effectively:
Modify your diet
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals to reduce the pressure on your stomach.
- Limit trigger foods and beverages such as spicy foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, and acidic foods like tomatoes and citrus fruits, as they can exacerbate symptoms.
- Increase fibre intake to help regulate digestion and reduce constipation, which can contribute to bloating and discomfort.
Adopt healthy lifestyle changes
- Maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight can increase abdominal pressure and worsen GORD symptoms.
- Quit smoking. Smoking weakens the lower oesophagal sphincter, contributing to the risk of acid reflux.
- Elevate the head of your bed by about 6-8 inches to help prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the oesophagus while sleeping.
Mindful eating practices
- Eat slowly and chew your food thoroughly to aid digestion and reduce the intake of air, which can lead to gas and bloating.
- Avoid lying down immediately after eating. Wait at least 2-3 hours before lying down or going to bed to give your body time to digest.
Stay hydrated
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day, but avoid drinking large amounts during meals to prevent overdistension of the stomach.
Manage stress
- Engage in stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises. Stress can negatively affect your digestive system and exacerbate symptoms.
Consider over-the-counter solutions
- Antacids can provide quick relief by neutralizing stomach acid.
- H2 blockers and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) reduce the production of stomach acid and are effective for treating GORD symptoms.
- Consult with The Family Chemist
- Seek medical advice if your symptoms persist or worsen. A healthcare professional can diagnose properly and recommend appropriate treatment, including prescription medications or further investigations such as an endoscopy.
Implementing these strategies can significantly alleviate symptoms of GORD and improve your overall digestive health.
Hair loss
A concerning side effect for many, has been observed in patients using Mounjaro for weight management. While this may be distressing, weighing this risk against the benefits of weight loss and weight loss is crucial.
How to overcome hairloss?
Overcoming hair loss involves a multifaceted approach, focusing on both medical treatments and lifestyle modifications. Here are effective strategies that can help manage and potentially reduce hair loss:
- Consult The Family Chemist: The first step in addressing hair loss is to consult with a healthcare professional.
- Use MHRA-Approved medications: Consider medications that have been approved for hair loss treatment. Minoxidil and Finasteride, Dutasteride (Propecia) are two commonly prescribed medications. Minoxidil is a topical and/or oral treatment suitable for men, while Finasteride is an oral medication primarily used by men. Dutasteride is another option, similar to Finasteride but not MHRA-approved for hair loss, though it’s used off-label.
- Incorporate a nutritious diet: A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support hair health. Focus on foods high in vitamins A, C, D, E, zinc, iron, omega-3 fatty acids, and protein. These nutrients are vital for hair follicle health and can promote hair growth.
- Reduce stress: Chronic stress is a known contributor to hair loss. Engaging in stress-reduction activities such as exercise, yoga, meditation, or any relaxing hobby can help mitigate hair loss.
- Avoid harsh hair treatments: Minimize the use of harsh chemical treatments, heat styling tools, and tight hairstyles that can contribute to hair breakage and loss. Opt for gentle hair care routines and products.
- Scalp massage: Regular scalp massages may increase blood flow to the scalp, promoting hair growth. This can be done during hair washing or when applying hair products.
- Natural remedies and supplements: While more research is needed, some studies suggest that certain supplements and natural remedies may support hair growth. These include saw palmetto, pumpkin seed oil, and biotin. However, it’s crucial to discuss these options with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
- Stay hydrated and get adequate sleep: General health practices such as staying hydrated and ensuring you get enough sleep can also impact hair health.
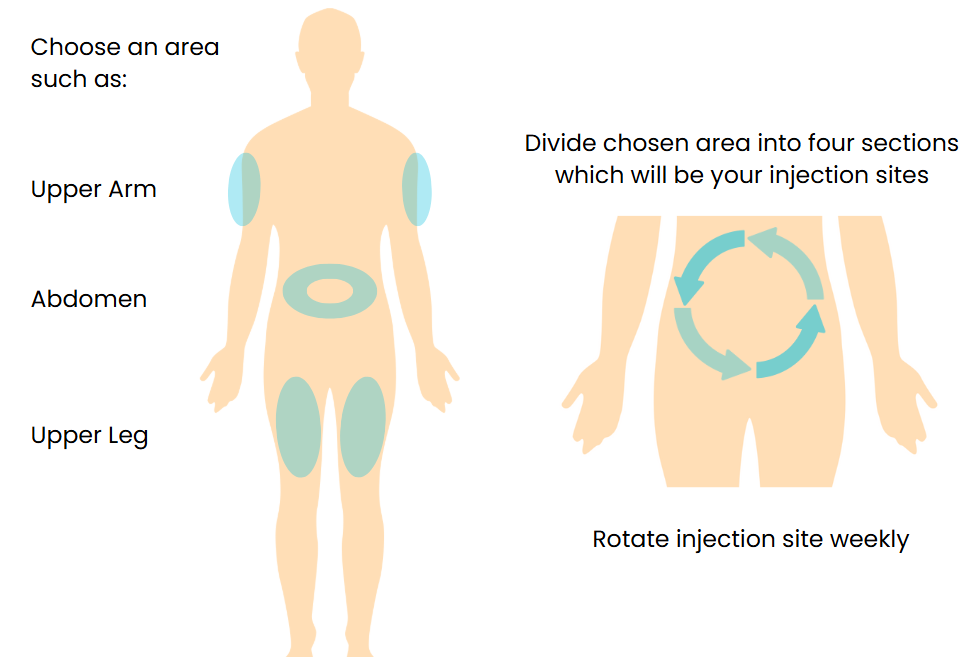
Fatigue, injection site reactions (such as itching or redness), a fast pulse, and increased levels of pancreatic enzymes in the blood are also among the common side effects listed.
Understanding these side effects is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. It enables informed decision-making and preparation for managing any adverse reactions that may arise. Always discuss any concerns or symptoms with a healthcare provider to ensure the best possible outcomes while using Mounjaro.
Conclusion
While Mounjaro showcases promising benefits in controlling appetite and improving metabolic health, awareness and management of its side effects are crucial for maximising its potential. Strategies to manage low blood sugar, allergic reactions, digestive issues, and hair loss ensure patient well-being and enhance treatment efficacy. By adopting a proactive approach to side effects—through dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and medical guidance—patients can experience the full benefits of Mounjaro with minimised discomfort.
For a full list of possible side effects, please read through the Patient Information Leaflet.
Mounjaro FAQs
How long do Mounjaro side effects last?
The duration of Mounjaro side effects can vary based on individual responses and the specific side effects experienced. Common side effects like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and decreased appetite typically diminish as the body adjusts to the medication over weeks to months. However, if side effects persist or worsen, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Should I report the Mounjaro side effects to The Family Chemist?
It’s recommended to report them through the MHRA Yellow Card scheme. This platform allows patients and healthcare professionals to report and monitor side effects of medications, contributing to safer drug use. Reporting can be done online or via the Yellow Card app, ensuring any concerns are addressed and managed appropriately.
What are the serious side effects of Mounjaro?
Mounjaro can cause serious side effects, though they are less common. These include:
- Pancreatitis
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) when used with other diabetes medications
- Kidney problems, including kidney failure
- Severe gastrointestinal issues
- Gallbladder problems, including gallstones
- Allergic reactions, which can be severe and require immediate attention
If you experience symptoms indicative of these serious side effects, such as severe abdominal pain, unusual bruising or bleeding, or jaundice, seek medical attention immediately.
What Happens When You Stop Taking Mounjaro?
Upon discontinuation, you may experience a reversal of its effects, such as weight gain or a rise in blood sugar levels. It’s important to discuss any changes in your medication regimen with a healthcare provider to manage these potential outcomes effectively.
Who Should Not Take Mounjaro?
Mounjaro is not suitable for everyone. Individuals with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) should avoid it. Additionally, it’s not recommended for use in patients with a history of severe gastrointestinal disease, pancreatitis, or gallbladder disease.
Does Mounjaro have long term side effects?
As Mounjaro is relatively new, long-term side effects are still under investigation. Ongoing studies and post-marketing surveillance are crucial to understanding the full spectrum of long-term implications. Patients are encouraged to maintain regular check-ups to monitor their health while on Mounjaro.
Read our other Mounjaro blogs




Maintenance Therapy on Weight Loss Medications: Wegovy and Mounjaro