Why Women Are at Greater Risk of Developing a UTI
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common bacterial infections, affecting millions of people every year. While anyone can get a UTI, women are significantly more likely to develop one. But why is this the case? What are UTI symptoms? And why is it easier to diagnose, and seek UTI treatment for women?
What Is a UTI?
A UTI occurs when bacteria, usually E. coli from the bowel, enter the urinary tract and cause an infection. UTIs can affect different parts of the urinary system but usually involve the urethra and bladder (cystitis).
Symptoms can include:
- Pain or burning while urinating
- Pain or cramping in the groin or lower abdomen
- Increased frequency needing to pass urine
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
Why Are Women More at Risk?
Nearly 50% of women will suffer from a UTI at some point in their lifetime, compared to only 13-14% of men. There’s a significant difference, and clear reasons for this.
Shorter urethra
One of the main reasons is anatomy. A woman’s urethra is shorter than a man’s; typically around 4cm compared to 20cm. The shorter urethra means bacteria have a shorter distance to travel to reach the bladder, creating an easier path for bacteria and a UTI to develop.
Urethra position
The female urethra is closer to the anus, where bacteria like E. coli are found. This proximity increases the chances of bacteria entering the urinary tract, especially after wiping back to front, or during sexual activity.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during pregnancy or menopause, can affect the urinary tract’s natural defences against bacteria. Reducing oestrogen levels during menopause can alter the balance of healthy bacteria and increase risk of infection. Increased progesterone during pregnancy relaxes muscles, increasing the womb’s pressure on the bladder, which can reduce its capacity to hold urine.
Sexual activity
Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, which is why it is common for some women to experience a UTI after sex.
Because of these differences, UTIs are less common in men. When they do occur, they may be a sign of an underlying problem, such as an enlarged prostate or another urinary tract issue. This means a UTI in men often needs further investigation by a healthcare professional to rule out more serious causes.
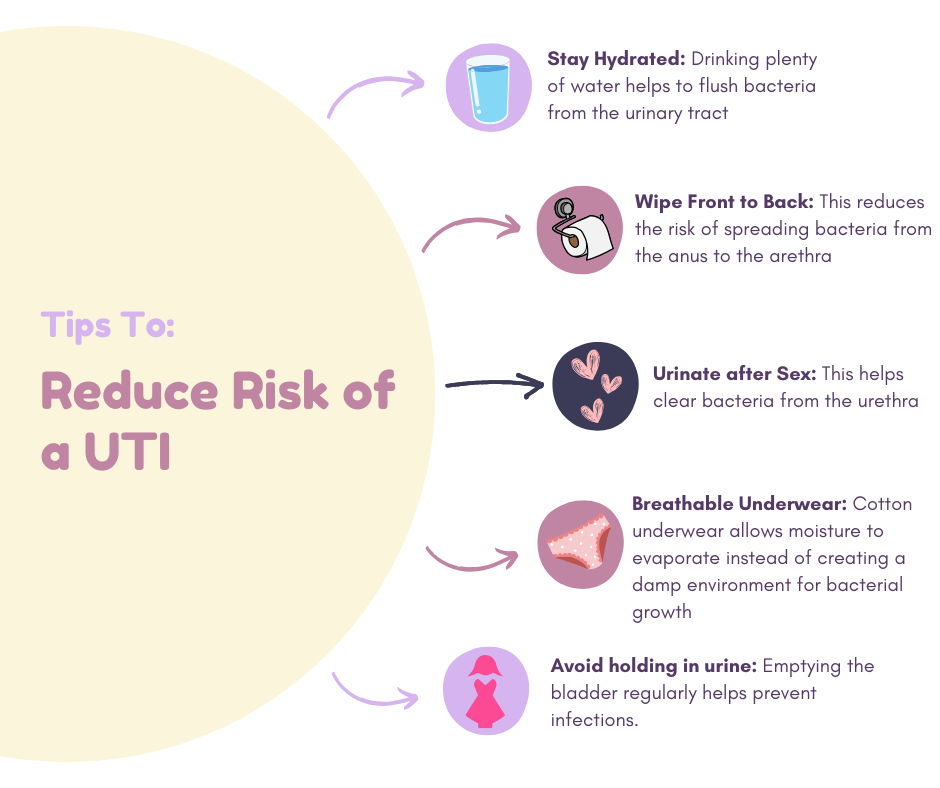
Reducing the Risk of a UTI
While women may be more prone to UTIs, there are steps that can help reduce the risk:
When to Seek Treatment for a UTI
If you think you have the symptoms of a UTI, treatments are available. Whether it’s to relieve discomfort caused by the acidity of urine or to take a short course of antibiotics to treat the infection, our treatments are effective, discreet and can help you seek relief quickly and safely.
The Bottom Line
Women are at greater risk of UTIs mainly due to anatomy and hormonal factors, but simple steps can help reduce the chance of infection. If you experience UTI symptoms, don’t wait; speak to a healthcare professional to get the right treatment.







