Does Vaping Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Table of Contents
Written by: Clara Hanson-Smith
Reviewed by: Sunny Dhain MPharmRS PgDip IndP
Date reviewed: 06/03/2024
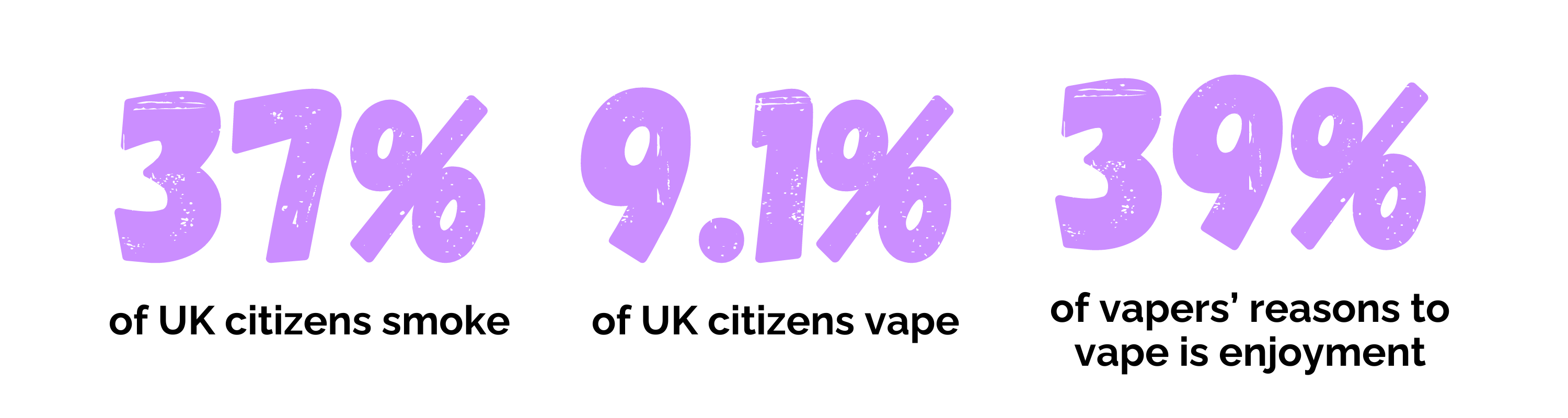
In recent years, there’s been a huge spike in vaping, particularly among younger people. Vaping, or the use of electronic cigarettes, has been researched for its impact on cardiovascular health, but its effects on sexual health, including ED, are gaining increasing attention. Today we cover how it causes erectile dysfunction, how to treat it and support available.
How does nicotine cause erectile dysfunction?
- Cardiovascular effects: E-cigarettes have been linked with cardiovascular effects, including increased blood pressure, heart rate, and arterial stiffness. These effects can block blood flow to the penis, which is essential for getting and keeping an erection.
- Nicotine: Many vapes contain nicotine, commonly known to restrict blood vessels and reduce blood flow. Nicotine can also affect the release of hormones and endogenous chemicals involved in the erectile response, potentially leading to ED.
- Endothelial dysfunction: E-cigarette use has been linked to endothelial dysfunction, which is the impairment of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. Endothelial dysfunction can lead to reduced nitric oxide production, a key role in getting an erection.
- Inflammation and oxidative stress: E-cigarette use has been associated with increased inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress can damage blood vessels and impair vascular function, causing ED.
- Psychological factors: The act of using vapes or concerns about their health effects may lead to stress, anxiety, or depression, which are known psychological factors associated with ED.
Am I at risk of ED if I Vape?
There is evidence to suggest that vaping, or vapes use, may increase the risk of ED through the mechanism of endothelial damage. The review highlights that vaping can induce aerobic stress, leading to endothelial damage, which in turn is considered a potential mechanism for ED.
While the review emphasizes the potential link between vaping and ED, it also notes that there is a lack of specific studies directly assessing this relationship. However, considering the known side effects of vaping on endothelial function, as well as the established link between endothelial dysfunction and ED, it is plausible that vaping may increase the risk of ED.
Therefore, based on the evidence, individuals who vape may be at risk of developing erectile dysfunction. However, further research, particularly clinical trials, is needed to establish a direct and comprehensive understanding of the relationship between vaping and ED.
Vaping vs smoking
Smoking’s effects on ED:
- Association with vascular changes: Smoking is one of the main reasons of vascular changes, and many cardiovascular risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and smoking have been linked to the development of ED.
- Impact on NO pathway: Smoking affects the nitric oxide (NO) signal transduction pathway, crucial for penile erection, by decreasing neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity and impairing endothelial NO-mediated vasodilation.
- Mechanism of action: Smoking increases the activity of Rho-associated kinase (ROK), which maintains the flaccid state of smooth muscle cells. Decreased NO levels due to smoking disinhibit ROK, further worsening ED.
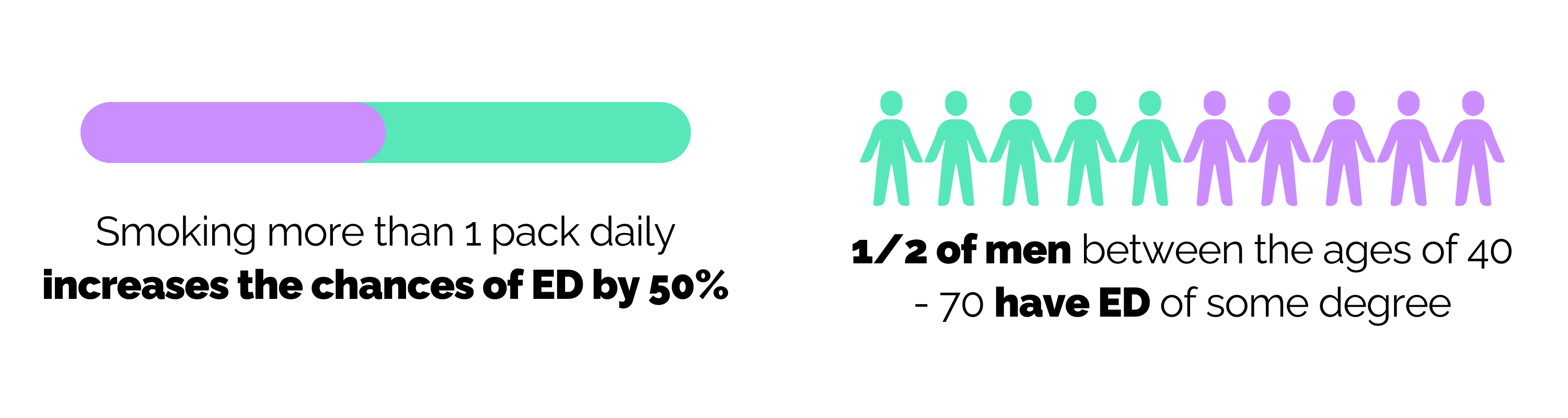
- Epidemiological links: Many studies have established a correlation between cigarette smoking and ED, with odds ratios ranging from 1.4 to 3.1 in various populations.
- Dose-dependency: The risk of developing ED appears to be dose-dependent, with heavier smokers and those with longer smoking histories having a higher likelihood of experiencing ED.
- Effects of smoking cessation: While some damage caused by smoking may be reversible, the magnitude of benefits from smoking cessation on ED is still debated. Studies suggest that younger men and those with less severe ED may have a better chance of erectile improvement after quitting smoking.
Vaping effects on ED
- Association with endothelial damage: Vaping can cause endothelial damage, potentially affecting erectile function. It also induces oxidative stress, leading to endothelial dysfunction, although further studies are needed to establish a direct link between vaping and ED.
- Potential mechanism: Endothelial dysfunction is suggested as a potential cause for ED. Vaping-induced oxidative stress and endothelial damage may contribute to ED, similar to the effects observed with cigarette smoking.
- Need for more research: While there is evidence linking vaping to endothelial damage, clinical trials specifically evaluating the relationship between vaping and ED are lacking.
Comparison:
- Mechanism of action: Both smoking and vaping appear to affect erectile function through vascular mechanisms by disrupting the nitric oxide pathway and causing endothelial damage.
- Evidence: Smoking has been more extensively studied, with epidemiological studies revealing a link between smoking and ED. Research on vaping and ED is still vague, with a need for more clinical trials to confirm the affects.
- Dose-dependency: Smoking shows a clear dose-dependent effect on the risk of developing ED, with heavier smokers and those with longer smoking histories having a higher risk. The dose-dependency of vaping on ED risk is less clear due to limited research.
- Effects of cessation: Quitting smoking has shown some potential for improving erectile function, especially in younger men and those with less severe ED. However, the effects of vaping cessation on ED are not well understood and require further investigation.
Other causes of impotence (ED)
Underlying health conditions
- Cardiovascular diseases include atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), hypertension (high blood pressure), and coronary artery disease.
- Diabetes can damage nerves and blood vessels involved in the erectile process.
- Neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries.
- Hormonal imbalances, including low testosterone levels.
- Chronic kidney disease.
- Obesity, which is linked to several health conditions that can contribute to ED
Medications
- Certain medications can interfere with erectile function as a side effect. These may include antidepressants, antihypertensives, antipsychotics, sedatives, corticosteroids, and medications for prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Lifestyle factors
Lifestyle choices can play a significant role in ED risk, including:
- Excessive alcohol consumption can impair sexual function and cause hormonal imbalances.
- Drug use, particularly illicit drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamines, and opioids.
- Poor diet and lack of exercise can contribute to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Psychological factors:
Psychological issues can contribute to or exacerbate ED, including:
- Stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Relationship problems or conflicts.
- Performance anxiety or fear of sexual failure.
- Low self-esteem or body image issues.
- Past traumatic sexual experiences.
- Age: As men age, they may experience changes in erectile function due to factors such as decreased testosterone levels, reduced blood flow to the penis, and the accumulation of underlying health conditions.
- Trauma or surgery: Trauma to the pelvic area or surgeries involving the prostate, bladder, or colon can damage nerves and blood vessels needed for achieving an erection.
- Sleep disorders: Conditions such as obstructive sleep apnoea, which disrupts normal breathing patterns during sleep, have been linked to ED.
- Psychiatric disorders: Conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, as well as specific treatments for these disorders, can contribute to sexual dysfunction.
Help with erectile dysfunction
- Medications: The Family Chemist provides a range of prescription erectile dysfunction medications, including sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra). These medications work by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating erections when sexual stimulation occurs. You can find more information and purchase these medications through The Family Chemist’s online platform.
- Quit smoking programs: The Family Chemist offers resources and support for smoking cessation, including Zyban and Champix, which are highly effective smoking cessation treatments. Quitting smoking can improve erectile function and overall cardiovascular health.
- Lifestyle changes: Besides medications and therapies, a healthy lifestyle can help improve ED. The Family Chemist can provide guidance on lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, stress management techniques, and limiting alcohol consumption.