Buy Lariam (Mefloquine) online in the UK for Malaria Prevention
The Family Chemist offers a convenient and confidential way to purchase Lariam (Mefloquine) online in the UK for malaria prevention. Our online pharmacy ensures easy access to this trusted medication, supported by expert healthcare guidance and comprehensive customer care.
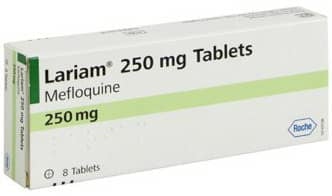
What is Lariam (Mefloquine) for Malaria Prevention?
Lariam (Mefloquine) is a prescription medication specially designed to prevent malaria when traveling to regions where the disease is prevalent. It belongs to the class of antimalarial drugs and is highly effective in reducing the risk of malaria infection.
What are the benefits of Lariam (Mefloquine) for Malaria Prevention?
Opting for Lariam (Mefloquine) offers several key benefits:
- Proven malaria prevention: Clinically proven to be highly effective in preventing malaria when taken as directed.
- Convenient dosage: Available in tablet form, making it easy to take before, during, and after travel to malaria-prone areas.
- Prescription-only: Available with a prescription from a healthcare professional to ensure proper use and dosage.
- Expert guidance: Receive guidance on malaria prevention and dosage instructions from our healthcare experts.